Navigating parental childcare leave in Singapore can be confusing with its various types and eligibility requirements. This comprehensive guide breaks down everything you need to know about Singapore parental childcare leave, helping you understand your entitlements and how to access them.
Types of Parental Leave in Singapore
Singapore offers several types of parental leave to support working parents:
Maternity Leave provides 16 weeks for working mothers of Singapore citizen children. The government fully funds the first two births, while for subsequent births, employers cover the first 8 weeks, and the government funds the remaining period.
Paternity Leave currently offers 2 weeks of mandatory Government-Paid Paternity Leave (GPPL). From January 1, 2024, fathers are entitled to four weeks of government-paid paternity leave.
Childcare Leave includes 6 days of paid leave annually for parents with children under 7 years old, and 2 days of extended paid childcare leave for parents with children between 7-12 years old.
Shared Parental Leave allows fathers to share up to 4 weeks of the mother’s 16-week maternity leave entitlement, giving both parents more flexibility in childcare arrangements.
Unpaid Infant Care Leave provides 6 days of unpaid leave per year for each parent with children under 2 years old, offering additional flexibility for parents of infants.

Childcare Leave Entitlements
Government-Paid Childcare Leave (GPCL)
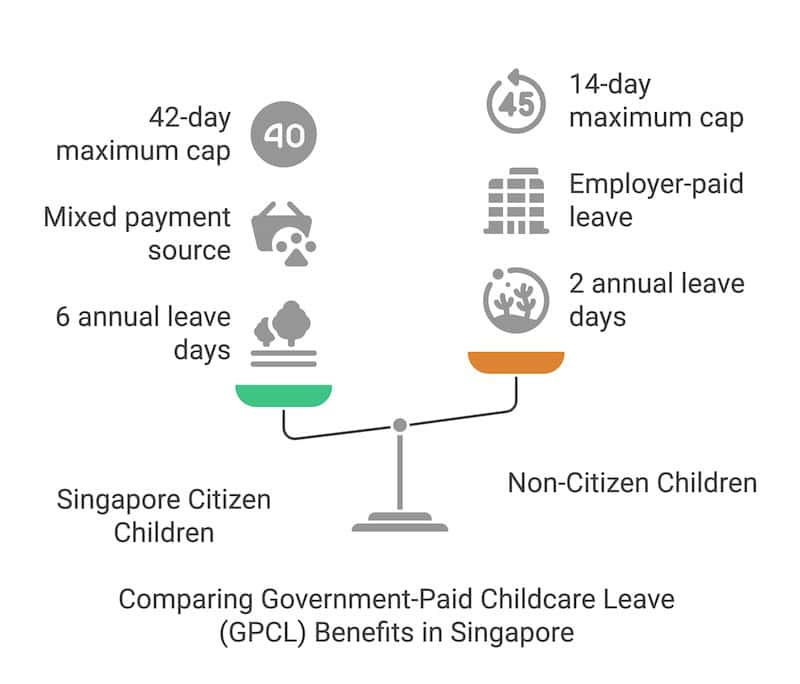
Government-Paid Childcare Leave provides eligible working parents with time off to care for their children. For Singapore citizen children:
Parents are entitled to 6 days of paid childcare leave each year until their child reaches 7 years old
The first three days are employer-paid at your gross rate of pay
For working mothers, the 4th, 5th and 6th day is fully supported by Government, with a daily allowance of up to $500 (total benefit of $1,500 per year, inclusive of CPF contributions)
Maximum cap of 42 days of childcare leave for each parent over a seven-year period
For non-citizen children under 7 years old:
2 days of paid childcare leave annually
Fully paid by the employer
Maximum cap of 14 days for each parent
Extended Childcare Leave (ECL)
When your Singapore citizen child is between 7 and 12 years old, you are entitled to:
2 days of Extended Childcare Leave per year
Fully Government-paid, capped at $500 per day (total of $1,000 per year)
Same eligibility criteria as GPCL regarding employment duration
Important notes about childcare leave:
Leave is provided on a per-year basis and cannot be carried forward
By default, the leave year follows the calendar year (January 1 to December 31)
You may agree with your employer to use a different 12-month period
GPCL is pro-rated according to your length of employment within the year
Both parents can claim entitlements independently if eligible
Eligibility Requirements
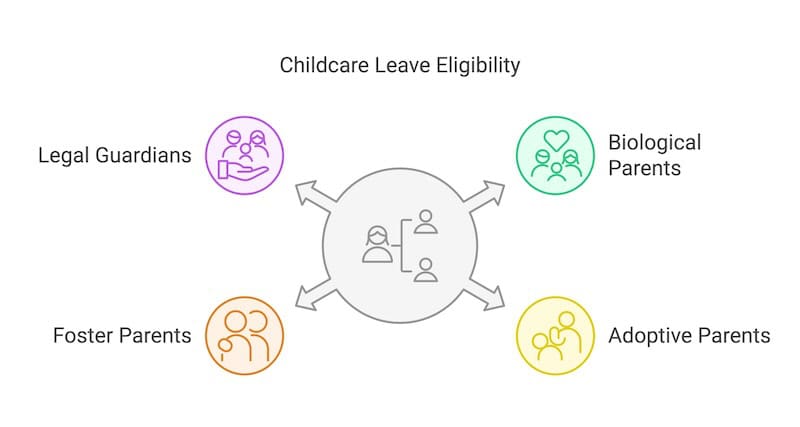
To qualify for Government-Paid Childcare Leave, you must meet these criteria:
Have at least one Singapore citizen child under 7 years old (for GPCL) or between 7-12 years old (for ECL)
Have served your employer for a continuous period of at least three months
For self-employed individuals: have been engaged in your business, trade, profession, or vocation for at least three continuous months
Adoptive Parents
Adoptive parents are eligible for childcare leave if they have legally adopted a child who is a Singapore citizen and meets the age requirements. The adoption must be formalized through a court adoption order.
Foster Parents
Foster parents are also eligible for childcare leave benefits if they:
Are officially recognized by the Ministry of Social and Family Development (MSF) Fostering Service
Can provide a Letter of Identity confirming their status as a foster parent
Are caring for a child under 7 years old (for GPCL) or between 7-12 years (for ECL)
Employers can verify foster parent eligibility by contacting MSF Fostering Service at [email protected].
Legal Guardians
Legal guardians appointed by court order can claim childcare leave if they:
Have legal custody of a Singapore citizen child under 7 years (for GPCL) or between 7-12 years (for ECL)
Can provide the Legal Guardianship document issued by the court
Meet other standard eligibility criteria regarding employment duration
Application Process
Required Documentation
Employees must submit the following documents to their employer for verification:
Completed GPCL1 declaration form
Child’s birth certificate (not required for foster parent/kin carer)
Singapore citizenship certificate of child (if applicable)
Letter of Identity for foster parent/kin carer (if applicable)
Legal Guardianship document (if applicable)
Notice Period Requirements
While there’s no statutory notice period specified in the law, it’s good practice to:
Provide reasonable notice to your employer
Follow your company’s leave application procedures
Plan your childcare leave in advance when possible
Employer’s Right to Verification
Employers have both the right and responsibility to verify an employee’s eligibility:
They must ensure employees meet all eligibility criteria
They need to collect and verify documentation
They must maintain records for 5 years from the last GPCL/ECL date
They can use their own form or system to capture employee declarations
Employers can refuse childcare leave if:
The employee has already used their full entitlement
The employee doesn’t meet eligibility requirements
Required documentation is incomplete or invalid
Online Application Systems
Many companies now use digital systems for leave applications. Check with your HR department about the specific procedures for applying for childcare leave through your company’s system.
Special Circumstances
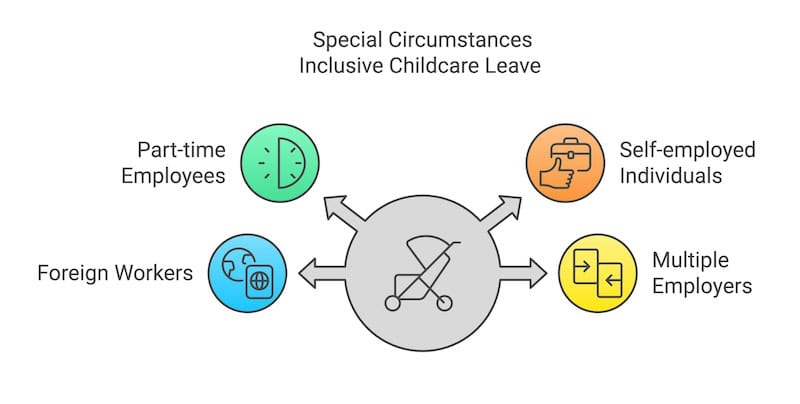
Part-time Employees
Part-time employees are eligible for childcare leave if they meet the basic eligibility criteria. Their entitlement is pro-rated based on their work schedule:
For Extended Childcare Leave, if a part-time employee works 5 hours daily, they would be entitled to 10 hours of leave (2 days × 5 hours)
This calculation applies similarly to the 6 days of regular childcare leave
Self-employed Individuals
Self-employed parents can claim childcare leave if they:
Have been engaged in their business, trade, profession, or vocation for at least 3 continuous months
Can demonstrate they have lost income during the childcare leave period
They receive the same entitlements as employed parents based on their child’s citizenship and age.
Foreign Workers in Singapore
Foreign workers (including Permanent Residents) are eligible based on their child’s citizenship status:
For children who are Singapore citizens:
6 days of GPCL for children under 7 years
2 days of ECL for children aged 7-12 years
For children who are not Singapore citizens:
2 days of paid childcare leave for children under 7 years
No extended childcare leave entitlement
Multiple Employers
For employees with multiple employers:
They cannot exceed their total annual childcare leave entitlement across all employers
They must declare previous childcare leave taken when applying with a current employer
When changing jobs within the same calendar year:
Employees must declare previous childcare leave taken
The new employer will consider the remaining leave balance
Employees cannot use job changes to claim additional leave
Employer Obligations and Employee Rights
Employers have several obligations regarding childcare leave:
They must grant childcare leave to eligible employees
They cannot terminate or threaten to terminate an employee for taking childcare leave
They must maintain proper records of leave applications and supporting documents
Employees have the right to:
Apply for and take childcare leave if they meet eligibility requirements
Receive their salary during the leave period according to the payment structure
Not face discrimination or unfair treatment for exercising their childcare leave rights
Salary Computation During Leave
For the employer-paid portion of childcare leave (first three days):
Full-time employees receive their gross rate of pay
Part-time employees receive pay proportional to their working hours
For the government-paid portion (fourth to sixth days for GPCL and both days for ECL):
Payment is capped at $500 per day
This includes the employer’s CPF contribution
Conclusion
Singapore’s parental childcare leave policies reflect the government’s commitment to supporting working parents and promoting work-life balance. Both Government-Paid Childcare Leave and Extended Childcare Leave provide valuable time for parents to care for their children during important developmental years.
Understanding your entitlements and the application process helps ensure you can fully utilize these benefits. If you need more information, visit the Ministry of Manpower website or contact the Tripartite Alliance for Fair and Progressive Employment Practices (TAFEP) for guidance.








